Course
Cell Biology
Study Pack
Set 16 The Cytoskeleton
Question 1
(Short Answer)
Free
According to the following graph, which shows the elongation rate at the plus and minus ends of actin filaments as a function of actin subunit concentration, at what concentration (A to E) does the total length of the filament remain more or less constant with time (i.e. steady-state treadmilling occurs)? 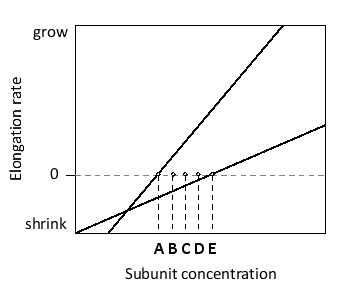

Answer
The line with the greater slope corresp...
View full Answer
Question 2
(Multiple Choice)
Free
In the polymerization in vitro of actin filaments and microtubules from their subunits, what does the "lag phase" correspond to?
A) Nucleation
B) Reaching steady state
C) Nucleotide exchange
D) ATP or GTP hydrolysis
E) Treadmilling
Answer
Question 3
(Short Answer)
Free
Consider the ATP-bound and ADP-bound forms of actin and the polarized nature of the actin filaments. In the following diagram that shows the various actin polymerization rate constants (k?n and k?ff values), which monomer corresponds to an ADP-bound actin incorporated at the plus end? 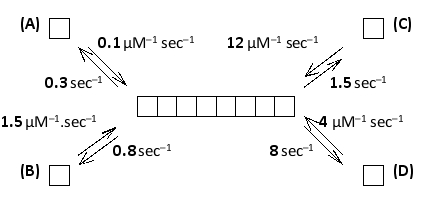

Answer
The plus end (right) has higher polymer...
View full Answer