Question 19
(Multiple Choice)
Note the location of the air bladders in the illustration below of the kelp; how might these structures represent an adaptive advantage? 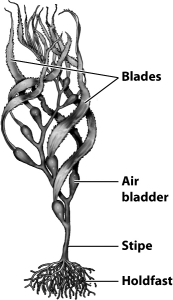
A)Kelp can live in deeper water, more distant from the surface, by storing carbon dioxide for future photosynthesis.
B)The bladders act like root nodules in terrestrial plants, housing the various organisms that convert dissolved nitrogen into forms usable by the kelp.
C)By acting as floats, the bladders aid in orienting the photosynthetic cells within the blade toward the surface and sunlight.
D)Waste gases can be stored within the bladders rather than polluting the habitat of the kelp.
Answer