Question 68
(Multiple Choice)
Use the following information to answer the questions below.
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)infects cells that have both CD4 and CCR5 cell surface molecules.The viral nucleic acid molecules are enclosed in a protein capsid,and the protein capsid is itself contained inside an envelope consisting of a lipid bilayer membrane and viral glycoproteins.One hypothesis for viral entry into cells is that binding of HIV membrane glycoproteins to CD4 and CCR5 initiates fusion of the HIV membrane with the plasma membrane,releasing the viral capsid into the cytoplasm.An alternative hypothesis is that HIV gains entry into the cell via receptor-mediated endocytosis,and membrane fusion occurs in the endocytotic vesicle.To test these alternative hypotheses for HIV entry,researchers labelled the lipids on the HIV membrane with a red fluorescent dye.
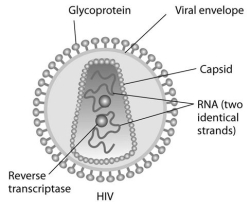
-Using live-cell fluorescence microscopy,researchers observed that a red fluorescent spot moved from the plasma membrane into the interior of target cells when red fluorescent dye-labelled HIV was added to the cells.What is the best conclusion from these observations?
A)The hypothesis that HIV enters the cell via fusion with the target cell plasma membrane is proved.
B)The hypothesis that HIV enters the cell via fusion with the target cell plasma membrane is not supported.
C)The hypothesis that HIV enters the cell via endocytosis is proved.
D)The hypothesis that HIV enters the cell via endocytosis is not supported.
E)Neither hypothesis is supported by these results.
Answer