Question 31
(Short Answer)
Two haploid budding yeast cells are allowed to mate. One of them carries a mutation in its mitochondrial DNA that makes the yeast cell resistant to an antifungal drug. If the resulting diploid zygote is allowed to propagate (in the absence of the drug), how do you predict that the fraction of drug-resistant cells will change over time in the population? Choose the best curve (A to F) from the following graph. Note that the "population" is only composed of one cell at the beginning of the experiment. The curves are smoothened to cancel stochastic fluctuations that happen at such low population sizes. 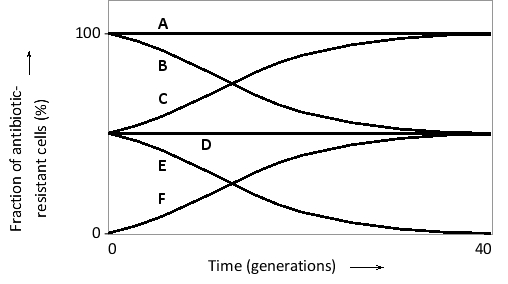
Answer
The zygote is resistant to the drug. Ho...
View full Answer