Question 31
(Multiple Choice)
You are studying the cellular basis of petal coloration in the flowering plant Ipomoea tricolor. These plants have colorful petals due to the presence of pH-sensitive vacuolar anthocyanins that change color from red/purple in acidic pH to blue at neutral pH. You treat petals with either vanadate (a specific inhibitor of P-ATPases) or bafilomycin (a specific inhibitor of V-ATPases) or both and compare the color with that of control petals, obtaining the results shown in the table below. Which of the following conclusions is consistent with these observations? 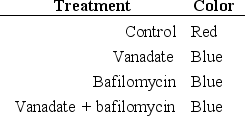
A) Both P- and V-ATPases are required to sufficiently acidify the vacuoles in petal cells.
B) P-ATPases are sufficient for acidification of the vacuoles in petal cells.
C) V-ATPases are sufficient for acidification of the vacuoles in petal cells.
D) Neither P- nor V-ATPases are necessary for vacuole acidification in petal cells.
Answer