Question 29
(Multiple Choice)
The specificity of nucleic acid hybridization is remarkable. Even a single mismatch between a probe and a target sequence can be detected depending on hybridization conditions. This sensitivity can be employed in applications such as SNP haplotyping. Consider a probe that is complementary to a 20-nucleotide-long genomic region including a single polymorphic nucleotide. The probe is perfectly complementary to the more common allele, but has one mismatch in the case of the minor allele. The temperature-dependent hybridization of the probe to the single-strand genomic fragment is schematically presented in the following graph. To detect hybridization, a fluorescent dye is added to the reaction. The dye fluoresces strongly only when intercalated between the bases of double-stranded DNA, and is therefore used to quantify double-strand formation or dissociation. Which "melting curve" (1 or 2) in the graph do you think corresponds to the more common SNP allele? Which curve shows a higher melting temperature? 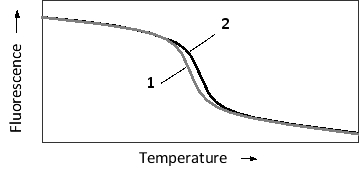
A) 1; 1
B) 1; 2
C) 2; 1
D) 2; 2
Answer