Question 50
(Short Answer)
Phylogenetic trees based on nucleotide or amino acid sequences can be constructed using various algorithms. One simple algorithm is based on a matrix of pairwise genetic distances (divergences) calculated after multiple alignment of the sequences. Imagine you have aligned a particular gene from different hominids (humans and the great apes), and have estimated the normalized number of nucleotide substitutions that have occurred in this gene in each pair of organisms since their divergence from their last common ancestor. You have obtained the following distance matrix.
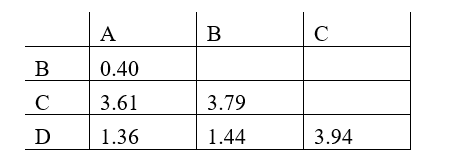
Answer the following question(s) based on this matrix.
-If species A in the distance matrix represents human, indicate which of the other species (B to D) represents chimpanzee, gorilla, and orangutan, respectively. Your answer would be a three-letter string composed of letters B, C, and D only, e.g. DCB.
Answer
The lowest pairwise distance in the mat...
View full Answer