Question 25
(Short Answer)
You have performed a chromosome conformation capture (3C) experiment to study chromatin looping at a mouse gene cluster that contains genes A, B, and C, as well as a regulatory region R. In this experiment, you performed in situ chemical cross-linking of chromatin, followed by cleavage of DNA in the nuclear extract with a restriction enzyme, intramolecular ligation, and cross-link removal. Finally, a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was carried out using a forward primer that hybridizes to a region in the active B gene, and one of several reverse primers, each of which hybridizes to a different location in the locus. The amounts of the PCR products were quantified and normalized to represent the relative cross-linking efficiency in each analyzed sample. You have plotted the results in the graph below. The same experiment has been done on two tissue samples: fetal liver (represented by red lines) and fetal muscle (blue lines).
Interaction of the A, B, and C genes with the regulatory R region is known to enhance expression of these genes. Indicate true (T) and false (F) statements below based on the results. Your answer would be a four-letter string composed of letters T and F only, e.g. TTTF.
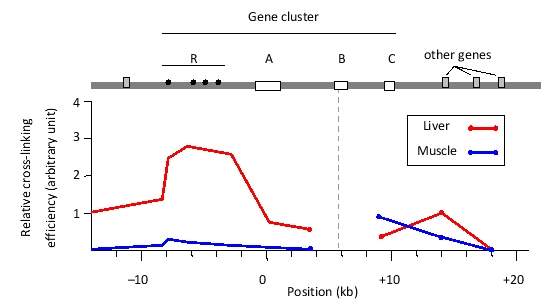
( ) The B gene would be predicted to have higher expression in the fetal liver compared to the fetal muscle tissue.
( ) Interaction between the R region and the B gene involves the A gene looping out.
( ) Interaction between the R region and the B gene involves the C gene looping out.
( ) In fetal muscle, the B gene definitely does not engage in looping interactions with any other elements in the cluster.
Answer
The 3C data show high relative cross-l...
View full Answer