Question 99
(Multiple Choice)
Mutant fruit flies that make only one antimicrobial peptide were tested for survival after infection with Neurospora crassa fungi or with Micrococcus luteus bacteria.
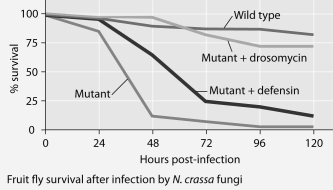
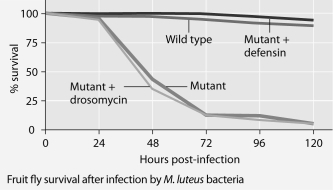
-The results shown in the graphs support the hypothesis that
A) adding the defensin gene to such mutants protects them from fungal infection.
B) adding the drosomycin gene to such mutants protects them from fungal infection.
C) wild-type flies with the full set of genes for antimicrobial peptides are highly susceptible to these infective agents.
D) the presence of any single antimicrobial peptide protects against both infective agents.
E) even the wild-type flies rarely, if ever, survive for five days.
Answer