Question 52
(Multiple Choice)
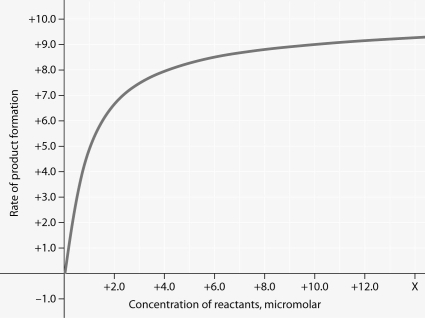
Rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction as a function of varying reactant
concentration, with the concentration of enzyme constant.
-For the enzyme-catalyzed reaction shown in the figure, which of these treatments will cause the greatest increase in the rate of the reaction, if the initial reactant concentration is 1.0 micromolar?
A) doubling the activation energy needed
B) cooling the reaction by 10°C
C) doubling the concentration of the reactants to 2.0 micromolar
D) doubling the enzyme concentration
E) increasing the concentration of reactants to 10.0 micromolar, while reducing the concentration of enzyme by 1/2
Answer